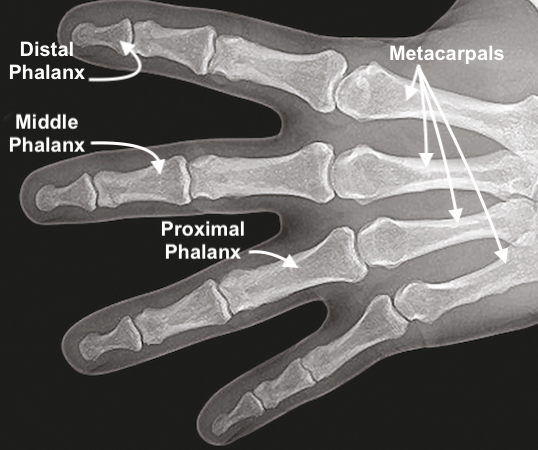
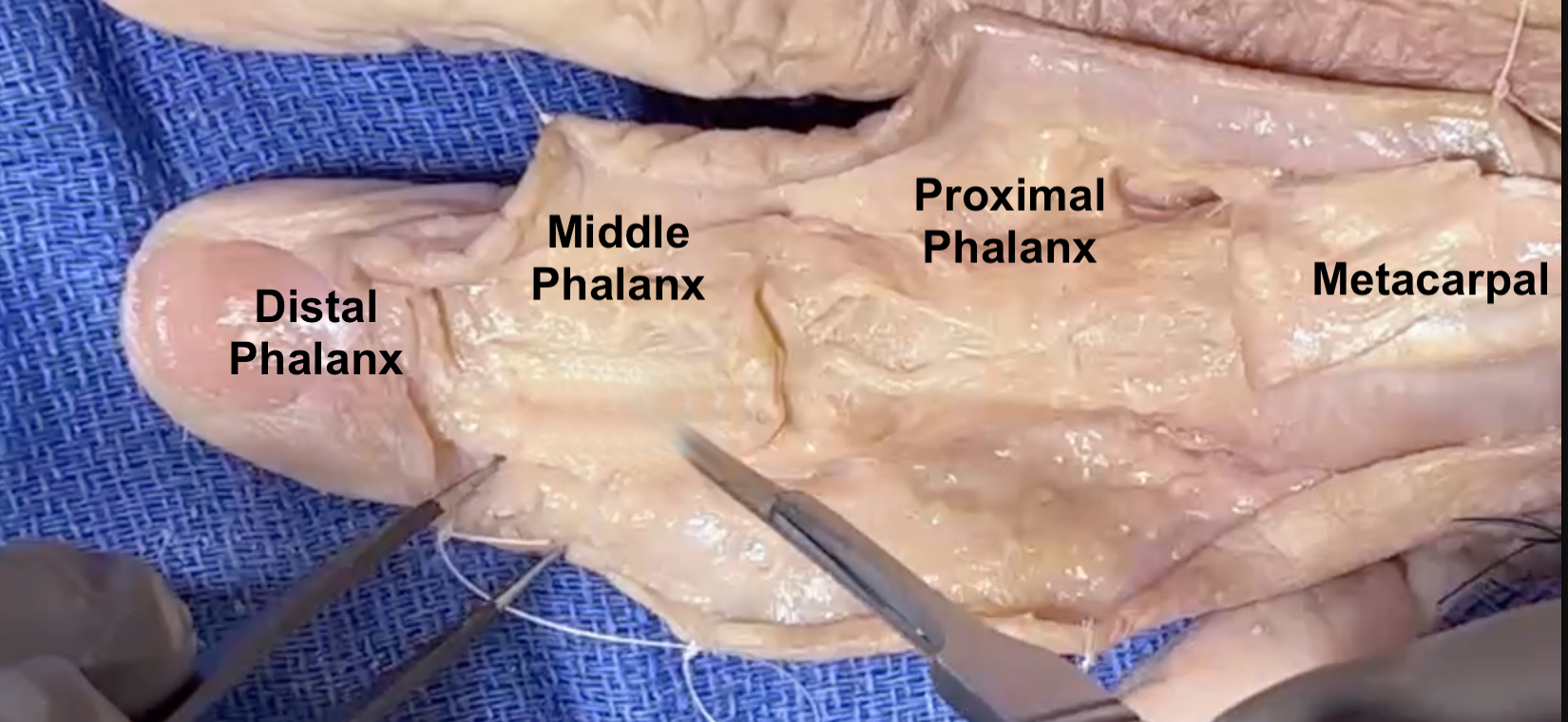
Proximal Phalanx Anatomy
Description:
- The proximal phalanges are small long bones of the fingers.
- The base of the proximal phalanx, which is part of the MP joint, and the distal head, which is part of the PIP joint, are covered with articular cartilage.
- The proximal phalanx has five basic parts: The head or distal epiphysis, the neck or metaphysis, the shaft or diaphysis, the proximal metaphysis, and the base or proximal epiphysis.
- The concave proximal ends of the proximal phalanx articulate with the metacarpals.
- The distal end of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th proximal phalanges articulate with the base of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th middle phalanges.
Diagrams & Photos
Key Points
- The fossae on the radial and ulnar sides of the proximal phalanx head are the origin site of the PIP joint collateral ligaments.
- The head of the proximal phalanx has two condyles with a shallow intercondylar groove.
- The shaft of the proximal phalanx is slightly convex dorsally and concave volarly.
- In the growing child there is an epiphyseal plate in the base of the proximal phalanx.
- The only muscles that insert into the proximal phalanx are the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th interossei muscles.